
4th June 2015 by aegeuana_sjp_admin
An Introduction to Metadata [PART 1]
In it’s simplest terms, metadata is data that describes other data. “Meta” is a Greek prefix used in English to denote a concept which is an abstraction of another concept.
Metadata summarizes basic information about data, such as the author, date created and modified, file size and more. Any file you find on your computer contains data about itself, like word, powerpoint, excel documents as well as image files, video files and more. The metadata from these files makes it easier to organize them and to find specific files faster, much like how a library would use metadata as a means of cataloging books.
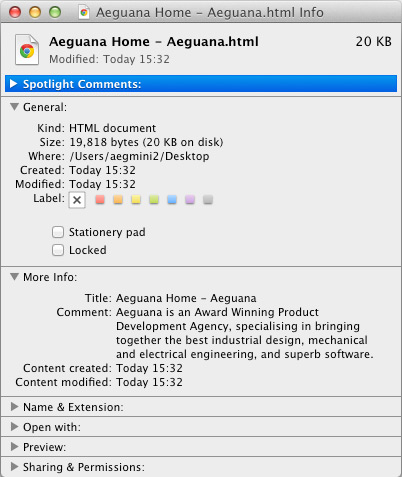
Additionally, websites can also contain metadata as they are files just the same. Web browsers and search engines use this information to help users what they’re looking for. Like normal computer files, a web page’s metadata can contain information like the author, the last modified date, et cetera, but it can also contain other types of metadata like title, description and keywords – information that is key for search engine optimization. Making sure this information is accurate and relevant is crucial to make sure your website is reaching its target audience.
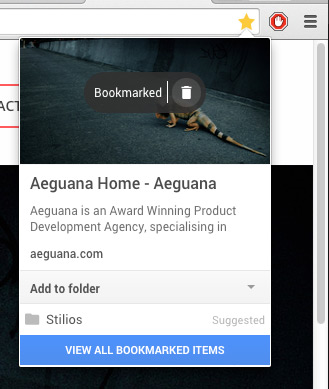
Web browsers can also use metadata. For example, if you save or bookmark a website using Google Chrome, the browser will capture the page’s description and use it as a criteria for users to search through their bookmarks. Chrome will also use the metadata to auto-categorize your website in Chrome’s new bookmark manager.
Adding metadata to your web pages is done through using meta tags in the <head> section of the HTML document. Multiple meta tags can be used to list various attributes. The image below contains an example of common meta tags found on most websites.
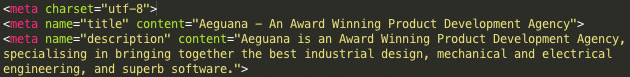
The charset attribute
This tells the browser how to display the page by specifying the character encoding used, with UTF-8 being the most broadly used.
The title attribute
This should not to be confused with the <title> html tag. Both of them specify the page name, however some search engines may use the meta title tag as the page name in the search results.
The description attribute
The description should contain a brief explanation of the content on the page in question. For subpages, it might be more specific and targeted, however on the homepage the description is generally a broader encapsulation of the website.
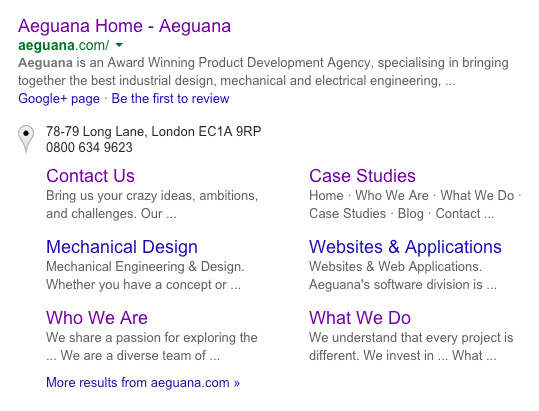
The result is as can be seen in the image below. Note that meta tags should be declared for every distinct subpage on your website.
This article continues here.




